In previous blogs, I wrote about running Kubernetes clusters in VMware Cloud Director using the Cluster API provider (CAPVCD) or Cluster API Provider for VMware Cloud Director (quite a mouthful). If you are interested in more background, you can check out these blogs:
- Cloud Native storage on VCD with the VMware Cloud Director CSI
- Cluster API with VMware Cloud Director 10.3 (CAPVCD), NSX-T and ALB
- VMware Cloud Director 10.3 refresh token and how to use them
Anyway, in this blog I want to discuss a feature that was introduced in VCD 10.4. Now we will not be discussing CAPVCD specifically (cluster API provider) but the Cloud provider component (CPI) whose purpose is to manage the lifecycle of the load balancers as well as associate Kubernetes nodes with virtual machines in the infrastructure.
Virtual service shared IP
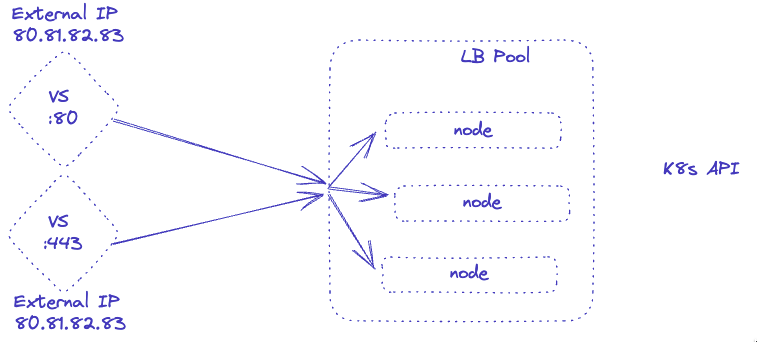
The new feature I am talking about is nothing really new but it exposes a capability of NSX ALB that allows you to share an IP between multiple virtual services. In earlier versions, a virtual service could only be assigned a unique IP address. Meaning if you wanted to expose port 80 and port 443 on the same IP for an ingress controller for instance, it wouldn’t work.
Note that this was never an issue for the load balancer used for the kubernetes API in 3 control-plane clusters as it only needs to reach the nodes on 1 port (6443 by default).
As a result, the maintainers used a workaround with a mix of one-arm load balancers and DNAT rules. That way, virtual services would have different “internal” IP addresses and multiple DNAT rule would translate the same external IP to these internal IPs.
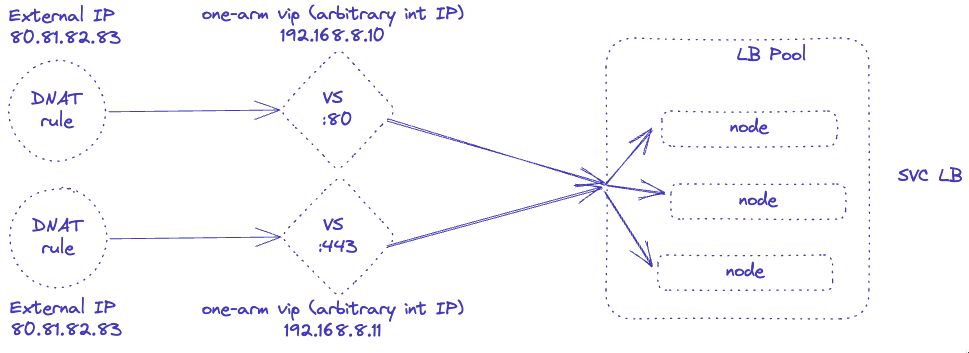
With the new NSX ALB feature, it is possible to share an IP among multiple virtual services, meaning the arbitrary internal IPs and DNAT rules are no longer needed.
Integration in cloud-provider-for-cloud-director
The Cloud Provider for VCD includes a way to enable this feature, however, note that it will apply to all kubernetes services (type LoadBalancer of course).
The enableVirtualServiceSharedIP flag is set in the configMap that contains the configuration of the CPI.
Note that the oneArm flag lets you influence the behaviour of the CPI as well.
There are 3 possible scenarios with these flags:
enableVirtualServiceSharedIP: trueandoneArm.enabled: false
A service type load balancer with multiple ports creates virtual services that share an IP from the Edge external pool. The environment must support virtual service shared IP (VCD 10.4 or xxx flag in AVI load balancer).
enableVirtualServiceSharedIP: trueandoneArm.enabled: true
A service type load balancer with multiple ports creates virtual services that share an internal IP (usually 192.168.8.x) with a NAT rule to map an IP from the Edge external pool to the internal IP. The environment must support virtual service shared IP (VCD 10.4 or xxx flag in AVI load balancer).
enableVirtualServiceSharedIP: falseandoneArm.enabled: true | false
A service type load balancer with multiple ports creates virtual services with different internal IPs (usually 192.168.8.x) with NAT rules to map an IP from the Edge external pool to the internal IPs. Compatible with versions older than VCD 10.4.
If the Cloud Provider is already deployed in your environment, just edit the configMap and then delete the pod to trigger its recreation so it loads the new content of the configMap.
CPI configMap
By default, the configMap is named vcloud-ccm-configmap (ccm stands for cloud controller manager).
kubectl get cm -n kube-system vcloud-ccm-configmap
NAME DATA AGE
vcloud-ccm-configmap 1 4d1h
You can then display its content to check what values are currently in place.
kubectl get cm -n kube-system vcloud-ccm-configmap -oyaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
vcloud-ccm-config.yaml: "vcd:\n host: https://my-vcd-endpoint\n org: my-org\n
\ vdc: my-vdc\nloadbalancer:\n network: my-network\n
\ vipSubnet: 80.81.82.80/28\n enableVirtualServiceSharedIP: true\n ports:\n
\ http: 80\n https: 443\n certAlias: NO_RDE_de59e3aa-a3d9-406d-bf65-7b385c7c99d3-cert\nclusterid:
NO_RDE_de59e3aa-a3d9-406d-bf65-7b385c7c99d3 \nvAppName: my-cluster\n"
Wrap up
I won’t go into the details of how to install the cloud provider as you probably already know how to do it if you are reading this. Note that work is currently under way to also support the feature to preserve client IP.
On a side note, if you are looking for options on how to protect your vSphere and VMware Cloud Director workloads, Nakivo Backup & Replication offers capabilities to back up vSphere VMs and VCD objects such as vApps, individual VMs and vApp metadata and ensure that remote workloads can be recovered in case of a data loss event.
